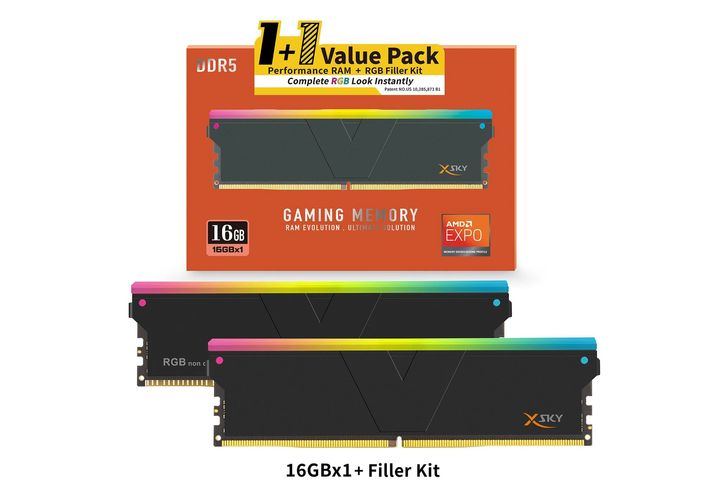

RAM kits are now sold with one fake RAM stick alongside a real one
Unscrupulous sellers are bundling fake RAM with real RAM to create an illusion of higher performance for AMD users, exploiting the ongoing memory shortage. This deceptive practice aims to provide desperate consumers with a temporary psychological relief as the supply crisis worsens.

Philosoph Jürgen Habermas Gestorben
Renowned German philosopher Jürgen Habermas, known for his influential contributions to critical theory and social philosophy, has passed away at the age of 96. Habermas was a leading figure in the Frankfurt School and his work explored the nature of modern society, political theory, and the importance of rational discourse in democratic processes.
Megadev: A Development Kit for the Sega Mega Drive and Mega CD Hardware
The article discusses the development of a megadev, a powerful AI system capable of self-improvement and unsupervised learning, and the ethical considerations surrounding its creation and use.

Starlink Militarization and Its Impact on Global Strategic Stability
The article explores the potential militarization of Starlink, SpaceX's satellite internet network, and its implications for global strategic stability. It discusses the dual-use nature of the technology and the concerns raised by its rapid deployment and use for military purposes.
![The Forth Language [Byte Magazine Volume 05 Number 08]](https://cdn.hazumi.news/eyJidWNrZXQiOiJoYXp1bWktaW1hZ2VzIiwia2V5IjoiNDczNzU5MzUiLCJlZGl0cyI6eyJyZXNpemUiOnsid2lkdGgiOjcyMCwiZml0IjoiY292ZXIifX19)
The Forth Language [Byte Magazine Volume 05 Number 08]
The August 1980 issue of Byte magazine features a wide range of articles covering topics such as microcomputer hardware, software, and applications, providing insights into the early days of the personal computing revolution.

What happens when US economic data becomes unreliable
The article discusses the potential challenges that can arise when US economic data becomes unreliable, including the impact on policymakers, businesses, and the public's understanding of the economy. It highlights the importance of accurate and trustworthy economic data for informed decision-making.

An Ode to Bzip
The article provides an in-depth exploration of the bzip2 compression algorithm, highlighting its efficient data compression capabilities, its historical significance, and its continued relevance in modern computing environments.

Jürgen Habermas, influential German philosopher, dies at 96
Jürgen Habermas, a renowned German philosopher and sociologist, has died at the age of 93. Habermas was a leading figure in the Frankfurt School of critical theory and is widely regarded as one of the most influential thinkers of the 20th century.

UBI Is Your Productivity Dividend – The Only Way to All Share What We All Built
The article discusses the potential benefits of universal basic income (UBI), arguing that it can increase productivity by reducing stress, allowing people to pursue more fulfilling work, and encouraging entrepreneurship and innovation.

Meta weighing 20% workforce layoffs to offset AI infrastructure costs: report
Meta is reportedly considering layoffs of up to 20% of its workforce, as the company aims to cut costs amid rising infrastructure expenses for its AI operations across its various platforms.

Show HN: AgentArmor – open-source 8-layer security framework for AI agents
I've been talking to founders building AI agents across fintech, devtools, and productivity – and almost none of them have any real security layer. Their agents read emails, call APIs, execute code, and write to databases with essentially no guardrails beyond "we trust the LLM."
So I built AgentArmor: an open-source framework that wraps any agentic architecture with 8 independent security layers, each targeting a distinct attack surface in the agent's data flow.
The 8 layers: L1 – Ingestion: prompt injection + jailbreak detection (20+ patterns, DAN, extraction attempts, Unicode steganography) L2 – Storage: AES-256-GCM encryption at rest + BLAKE3 integrity for vector DBs L3 – Context: instruction-data separation (like parameterized SQL, but for LLM context), canary tokens, prompt hardening L4 – Planning: action risk scoring (READ=1 → DELETE=7 → EXECUTE=8 → ADMIN=10), chain depth limits, bulk operation detection L5 – Execution: network egress control, per-action rate limiting, human approval gates with conditional rules L6 – Output: PII redaction via Microsoft Presidio + regex fallback L7 – Inter-agent: HMAC-SHA256 mutual auth, trust scoring, delegation depth limits, timestamp-bound replay prevention L8 – Identity: agent-native identity, JIT permissions, short-lived credentials
I tested it against all 10 OWASP ASI (Agentic Security Integrity) risks from the December 2025 spec. The red team suite is included in the repo.
Works as: (a) a Python library you wrap around tool calls, (b) a FastAPI proxy server for framework-agnostic deployment, or (c) a CLI for scanning prompts in CI.
Integrations included for: LangChain, OpenAI Agents SDK, MCP servers.
I ran it live with a local Ollama agent (qwen2:7b) – you can watch it block a `database.delete` at L8 (permission check), redact PII from file content at L6, and kill a prompt injection at L1 before it ever reaches the model.
GitHub: https://github.com/Agastya910/agentarmor PyPI: pip install agentarmor-core
Would love feedback, especially from people who have actually built production agents and hit security issues I haven't thought of.
TAGS: security, python, llm, ai, agents
The most SHAMELESS structural manipulation of a index I've ever seen
The article discusses the concept of 'thought leadership' and its potential pitfalls. It explores how thought leadership can become a tool for self-promotion and the importance of maintaining authenticity and adding value to one's audience.

Hundreds of GitHub Python Repos Compromised via Account Takeover and Force-Push
The article discusses a security incident where hundreds of GitHub Python repositories were compromised through account takeovers and force pushes, leading to the distribution of malicious code. It highlights the importance of secure software development practices and the need for developers to be vigilant in protecting their accounts and repositories.

A Swiss Paperwork Massacre: Why We Fled to Stripe
The article discusses the challenges faced by consumers and businesses due to payment processing issues, including delayed transactions, fraudulent activities, and the need for more secure and efficient payment solutions to address these problems.
Show HN: I built Wool, a lightweight distributed Python runtime
I spent a long time working in the payments industry, specifically on a rather niche reporting/aggregation platform with spiky workloads that were not easily parallelized. To pump as much data through our pipeline as possible, we had to rely on complex locking schemes across half a dozen or so not-so-micro services - keeping a clear mental picture of how the services interacted for a given data source was a major headache. This problem always intrigued me, even after I no longer worked at the company, and lead to the development of Wool.
If you've worked with frameworks like Ray or Prefect, you're probably familiar with the promise of going from script to scale in two lines of code (or something along those lines). This is essentially the solution I was looking for: a framework with limited boilerplate that facilitated arbitrary distribution schemes within a single, coherent codebase. What I was hoping for, though, was something a little bit more focused - I wasn't working on ML pipelines and didn't need much else other than the distribution layer. This is where Wool comes in. While it's API is very similar to those of Ray and Prefect, where it differentiates itself is in its scope and architecture.
First, Wool is not a task orchestrator. It provides push-based, best-effort, at-most-once execution. There is no built-in coordination state, retry logic, or durable task tracking. Those concerns remain application-defined. The beauty of Wool is that it looks and feels like native async Python, allowing you to use purpose-built libraries for your needs as you would for any other Python app (with some caveats).
Second, Wool was designed with speed in mind. Because it's not bloated with features, it's actually pretty fast, even in its current nascent state. Wool routines are dispatched directly to a decentralized peer-to-peer network of gRPC workers, who can distribute nested routines amongst themselves in turn. This results in low dispatch latencies and high throughput. I won't make any performance claims until I can assemble some more robust benchmarks, but running local workers on my M4 MacBook Pro (a trivial example, I know), I can easily achieve sub-millisecond dispatch latencies.
Anyway, check it out, any and all feedback is welcome. Regarding docs- the code is the documentation for now, but I promise I'll sort that out soon. I've got plenty of ideas for next steps, but it's always more fun when people actually use what you've built, so I'm open to suggestions for impactful features.
-Conrad

The United States of Eugenics
The article examines the historical and ongoing influence of eugenics in US politics, policies, and social attitudes, exploring its connections to racism, xenophobia, transphobia, and other forms of discrimination, particularly under the Trump administration's policies.
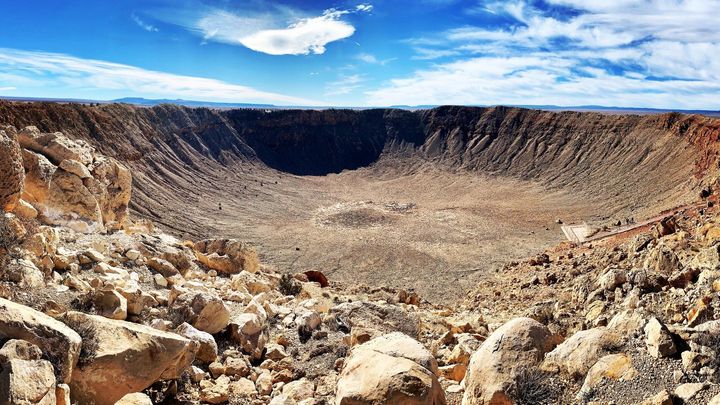

Arizona's Meteor Crater is still revealing new secrets 50k years later
The article discusses the ongoing scientific research at Arizona's Meteor Crater, which was formed by a meteorite impact over 50,000 years ago. Researchers continue to uncover new insights about the formation and composition of this iconic geological feature, shedding light on the dynamic processes that shaped the Earth's surface.

Jürgen Habermas died
Jürgen Habermas, a renowned German philosopher and sociologist, has passed away at the age of 96. Habermas was a leading figure in the Frankfurt School of critical theory and is known for his influential works on communicative action, the public sphere, and the critique of modernity.

Elite Russian squad targeting enemies abroad was exposed throug Google Translate
The article reports that Russia has created an elite hit squad to target its opponents abroad. One of the squad's agents was compromised after using Google Translate, revealing the group's existence.

Show HN: Markitdown in Go
Markitdown is an open-source library that provides a set of markdown-related utilities, including parsing, rendering, and converting markdown to HTML. It is designed to be lightweight, extensible, and easy to use in various programming languages.